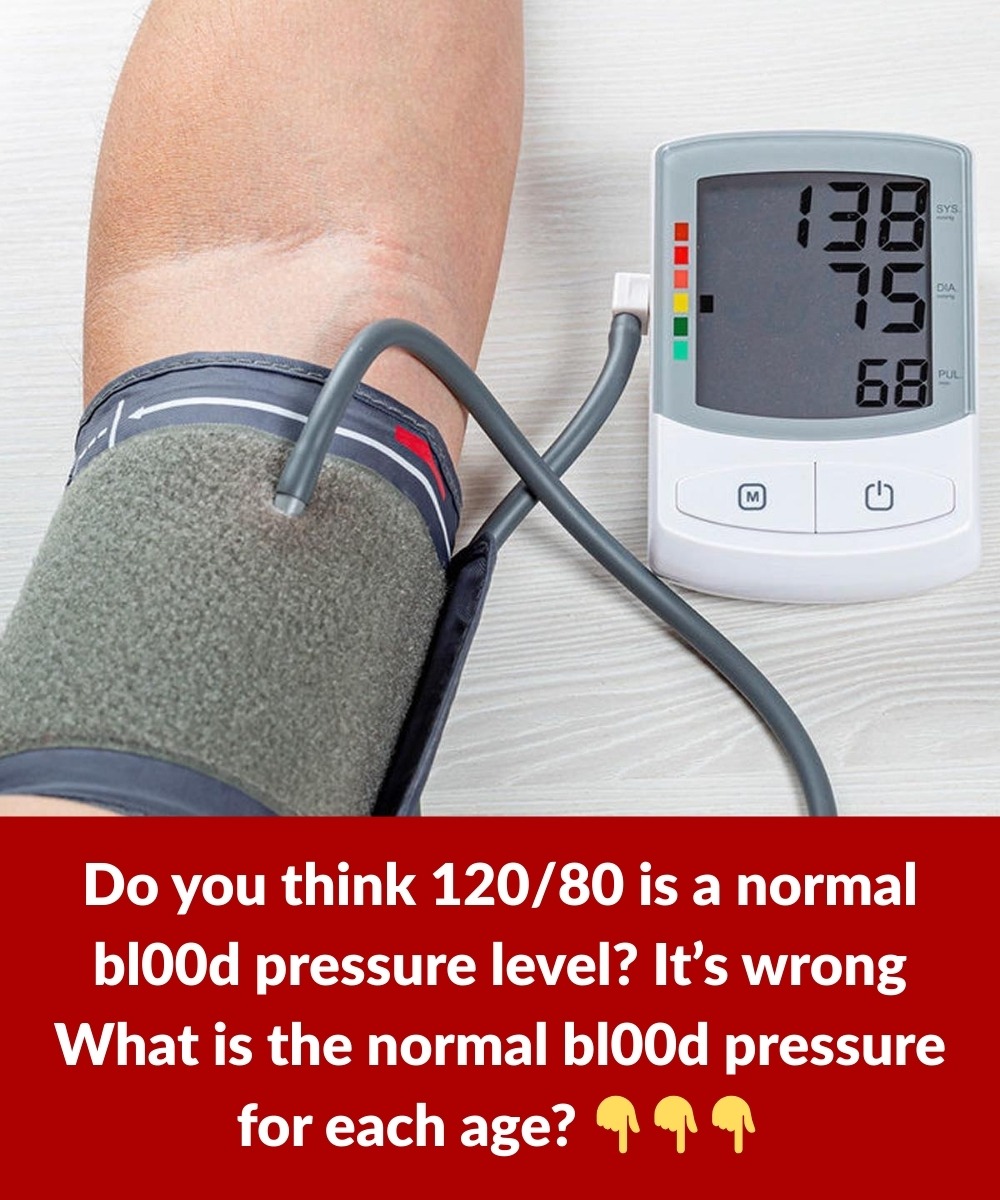
Blood pressure is a key indicator of your overall health. But did you know that what’s considered “normal” can change as you age? Understanding how age impacts your blood pressure—and knowing the healthy range for your age group—can help you take proactive steps to maintain good health and prevent serious conditions like heart disease and stroke.
Why bl00d pressure is cruciall
Bl00d pressure is the force of bl00d pushing against the walls of your arteries as the heart pumps blood around your body. Bl00d pressure readings can give an indication of how hard your heart is working and are an important part of a general health assessment.
A normal blood pressure varies from person to person. Your doctor will suggest you on what is healthy for you, based on your medical history.
For most people, the following is a guide.
Bl00d pressure Systolic (top number) mm Hg Diastolic (bottom number) mm Hg
Low Less than 90 Less than 60
Optimal Less than 120 Less than 80
Normal 120–129 80–84
Normal to high 130–139 85–89
High Greater than 140 Greater than 90
Around 120/80 mm Hg is often considered a typical blood pressure reading.
Below is the average bl00d pressure for children and teens:
Age Systolic (top number) mm Hg Diastolic (bottom number) mm Hg
Newborns up to 1 month 60–90 20–60
Infants 87–105 53–66
Toddlers 95–105 53–66
Preschoolers 95–110 56–70
School-aged children 97–112 57–71
Adolescents 112–128 66–80
In adulthood, the average bl00d pressures by age and gender are: